C# 코드로 접근하는 MethodDesc, MethodTable
windbg의 sos 확장에서 제공하는 dumpmd 등의 명령어를 이용할 때 자주 접근하게 되는 자료 구조가 바로 "MethodDesc"입니다. 재미있는 것은 이 값을 C# 코드에서도 MethodHandle 속성을 이용해 간단하게 구할 수 있다는 점입니다.
Program pg = new Program();
Action ivd = pg.Method;
Console.WriteLine($"MethodHandle == Method Desc: {ivd.Method.MethodHandle.Value.ToInt64():x}");
또한 MethodTable 값도 Type 속성의 TypeHandle을 통해 구할 수 있습니다.
Console.WriteLine($"TypeHandle == MethodTable: {ivd.Method.DeclaringType.TypeHandle.Value.ToInt64():x}");
실제로 저렇게 출력한 값을,
MethodHandle == Method Desc: 7fff2ba65dc8
TypeHandle == MethodTable: 7fff2ba65de0
windbg + sos 환경에 붙여 그대로 실습할 수 있습니다.
0:000> !dumpmd 7fff2ba65dc8
Method Name: MyMain`2[[System.Boolean, mscorlib],[System.Int32, mscorlib]].Method(Int32)
Class: 00007fff2bbf07f8
MethodTable: 00007fff2ba65de0
mdToken: 0000000006000056
Module: 00007fff2ba64148
IsJitted: yes
CodeAddr: 00007fff2bb70bc0
Transparency: Critical
0:000> !dumpmt -md 7fff2ba65de0
EEClass: 00007fff2bbf07f8
Module: 00007fff2ba64148
Name: MyMain`2[[System.Boolean, mscorlib],[System.Int32, mscorlib]]
mdToken: 0000000002000019
File: C:\ConsoleApp1\ConsoleApp1\bin\Debug\ConsoleApp1.exe
BaseSize: 0x18
ComponentSize: 0x0
Slots in VTable: 15
Number of IFaces in IFaceMap: 0
--------------------------------------
MethodDesc Table
Entry MethodDesc JIT Name
00007fff88573450 00007fff87ff8de8 PreJIT System.Object.ToString()
00007fff8858dc80 00007fff881bc180 PreJIT System.Object.Equals(System.Object)
00007fff88573090 00007fff881bc1a8 PreJIT System.Object.GetHashCode()
00007fff88570420 00007fff881bc1b0 PreJIT System.Object.Finalize()
...[생략]...
00007fff2bb70bc0 00007fff2ba65dc8 JIT MyMain`2[[System.Boolean, mscorlib],[System.Int32, mscorlib]].Method(Int32)
MethodDesc에 대한 좀 더 자세한 정보는 다음의 문서를 통해 확인할 수 있습니다.
Method Descriptor
; https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/master/docs/design/coreclr/botr/method-descriptor.md
MethodDesc (method descriptor) is the internal representation of a managed method. It serves several purposes:
Provides a unique method handle, usable throughout the runtime. For normal methods, the MethodDesc is a unique handle for a <module, metadata token, instantiation> triplet.
Caches frequently used information that is expensive to compute from metadata (e.g. whether the method is static).
Captures the runtime state of the method (e.g. whether the code has been generated for the method already).
Owns the entry point of the method.
There are multiple kinds of MethodDescs:
IL, Instantiated, FCall, NDirect, EEImpl, Array, ComInterop, Dynamic
중요한 것은 MethodDesc이 메서드의 종류에 따라 달라진다는 것인데 실제 코드를 통해 보면,
shared-source-cli-2.0/clr/src/vm/method.hpp
; https://github.com/fixdpt/shared-source-cli-2.0/blob/master/clr/src/vm/method.hpp
runtime/src/coreclr/src/vm/method.hpp
; https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/master/src/coreclr/src/vm/method.hpp
우선 일반적인 IL 메서드에 대응하는 MethodDesc 정의를 데이터 필드만 정리해 보면 다음과 같은 식입니다.
class MethodDesc
{
protected:
enum {
// There are flags available for use here (currently 5 flags bits are available); however, new bits are hard to come by, so any new flags bits should
// have a fairly strong justification for existence.
enum_flag3_TokenRemainderMask = 0x3FFF, // This must equal METHOD_TOKEN_REMAINDER_MASK calculated higher in this file
// These are seperate to allow the flags space available and used to be obvious here
// and for the logic that splits the token to be algorithmically generated based on the
// #define
enum_flag3_HasForwardedValuetypeParameter = 0x4000, // Indicates that a type-forwarded type is used as a valuetype parameter (this flag is only valid for ngenned items)
enum_flag3_ValueTypeParametersWalked = 0x4000, // Indicates that all typeref's in the signature of the method have been resolved to typedefs (or that process failed) (this flag is only valid for non-ngenned methods)
enum_flag3_DoesNotHaveEquivalentValuetypeParameters = 0x8000, // Indicates that we have verified that there are no equivalent valuetype parameters for this method
};
UINT16 m_wFlags3AndTokenRemainder;
BYTE m_chunkIndex;
enum {
// enum_flag2_HasPrecode implies that enum_flag2_HasStableEntryPoint is set.
enum_flag2_HasStableEntryPoint = 0x01, // The method entrypoint is stable (either precode or actual code)
enum_flag2_HasPrecode = 0x02, // Precode has been allocated for this method
enum_flag2_IsUnboxingStub = 0x04,
enum_flag2_HasNativeCodeSlot = 0x08, // Has slot for native code
enum_flag2_IsJitIntrinsic = 0x10, // Jit may expand method as an intrinsic
enum_flag2_IsEligibleForTieredCompilation = 0x20,
// unused = 0x40,
// unused = 0x80,
};
BYTE m_bFlags2;
// The slot number of this MethodDesc in the vtable array.
// Note that we may store other information in the high bits if available --
// see enum_packedSlotLayout and mdcRequiresFullSlotNumber for details.
WORD m_wSlotNumber;
enum {
enum_packedSlotLayout_SlotMask = 0x03FF,
enum_packedSlotLayout_NameHashMask = 0xFC00
};
WORD m_wFlags;
};
즉, sizeof(MethoDesc) == 8 바이트의 아주 가벼운 구조체입니다. 그다음 각각의 메서드 유형은 MethodDesc을 상속받아 개별 구성에 맞게 필드를 더 정의하는 식으로 확장합니다.
class StoredSigMethodDesc : public MethodDesc
{
public:
// Put the sig RVA in here - this allows us to avoid
// touching the method desc table when mscorlib is prejitted.
RelativePointer<TADDR> m_pSig;
DWORD m_cSig;
#ifdef HOST_64BIT
// m_dwExtendedFlags is not used by StoredSigMethodDesc itself.
// It is used by child classes. We allocate the space here to get
// optimal layout.
DWORD m_dwExtendedFlags;
#endif
};
class FCallMethodDesc : public MethodDesc
{
DWORD m_dwECallID;
#ifdef HOST_64BIT
DWORD m_padding;
#endif
};
class HostCodeHeap;
class LCGMethodResolver;
typedef DPTR(LCGMethodResolver) PTR_LCGMethodResolver;
class ILStubResolver;
typedef DPTR(ILStubResolver) PTR_ILStubResolver;
class DynamicResolver;
typedef DPTR(DynamicResolver) PTR_DynamicResolver;
class DynamicMethodDesc : public StoredSigMethodDesc
{
protected:
RelativePointer<PTR_CUTF8> m_pszMethodName;
PTR_DynamicResolver m_pResolver;
#ifndef HOST_64BIT
// We use m_dwExtendedFlags from StoredSigMethodDesc on WIN64
DWORD m_dwExtendedFlags; // see DynamicMethodDesc::ExtendedFlags enum
#endif
};
class ArrayMethodDesc : public StoredSigMethodDesc
{
};
class NDirectImportThunkGlue
{
PVOID m_dummy; // Dummy field to make the alignment right
public:
LPVOID GetEntrypoint()
{
LIMITED_METHOD_CONTRACT;
return NULL;
}
void Init(MethodDesc *pMethod)
{
LIMITED_METHOD_CONTRACT;
}
};
#ifdef FEATURE_PREJIT
PORTABILITY_WARNING("NDirectImportThunkGlue");
#endif // FEATURE_PREJIT
#endif // HAS_NDIRECT_IMPORT_PRECODE
typedef DPTR(NDirectImportThunkGlue) PTR_NDirectImportThunkGlue;
class NDirectWriteableData
{
public:
// The JIT generates an indirect call through this location in some cases.
// Initialized to NDirectImportThunkGlue. Patched to the true target or
// host interceptor stub or alignment thunk after linking.
LPVOID m_pNDirectTarget;
};
typedef DPTR(NDirectWriteableData) PTR_NDirectWriteableData;
class NDirectMethodDesc : public MethodDesc
{
public:
struct temp1
{
// If we are hosted, stack imbalance MDA is active, or alignment thunks are needed,
// we will intercept m_pNDirectTarget. The true target is saved here.
LPVOID m_pNativeNDirectTarget;
// Information about the entrypoint
RelativePointer<PTR_CUTF8> m_pszEntrypointName;
union
{
RelativePointer<PTR_CUTF8> m_pszLibName;
DWORD m_dwECallID; // ECallID for QCalls
};
// The writeable part of the methoddesc.
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
RelativePointer<PTR_NDirectWriteableData> m_pWriteableData;
#else
PlainPointer<PTR_NDirectWriteableData> m_pWriteableData;
#endif
#ifdef HAS_NDIRECT_IMPORT_PRECODE
RelativePointer<PTR_NDirectImportThunkGlue> m_pImportThunkGlue;
#else // HAS_NDIRECT_IMPORT_PRECODE
NDirectImportThunkGlue m_ImportThunkGlue;
#endif // HAS_NDIRECT_IMPORT_PRECODE
ULONG m_DefaultDllImportSearchPathsAttributeValue; // DefaultDllImportSearchPathsAttribute is saved.
// Various attributes needed at runtime.
WORD m_wFlags;
#if defined(TARGET_X86)
// Size of outgoing arguments (on stack). Note that in order to get the @n stdcall name decoration,
// it may be necessary to subtract 4 as the hidden large structure pointer parameter does not count.
// See code:kStdCallWithRetBuf
WORD m_cbStackArgumentSize;
#endif // defined(TARGET_X86)
// This field gets set only when this MethodDesc is marked as PreImplemented
RelativePointer<PTR_MethodDesc> m_pStubMD;
} ndirect;
};
class EEImplMethodDesc : public StoredSigMethodDesc
{ };
struct ComPlusCallInfo
{
union
{
// IL stub for CLR to COM call
PCODE m_pILStub;
// MethodDesc of the COM event provider to forward the call to (COM event interfaces)
MethodDesc *m_pEventProviderMD;
};
// method table of the interface which this represents
PTR_MethodTable m_pInterfaceMT;
// We need only 3 bits here, see enum Flags below.
BYTE m_flags;
// ComSlot() (is cached when we first invoke the method and generate
// the stubs for it. There's probably a better place to do this
// caching but I'm not sure I know all the places these things are
// created.)
WORD m_cachedComSlot;
#ifdef TARGET_X86
// Size of outgoing arguments (on stack). This is currently used only
// on x86 when we have an InlinedCallFrame representing a CLR->COM call.
WORD m_cbStackArgumentSize;
#else
LPVOID m_pRetThunk;
#endif
// This field gets set only when this MethodDesc is marked as PreImplemented
RelativePointer<PTR_MethodDesc> m_pStubMD;
};
class ComPlusCallMethodDesc : public MethodDesc
{
ComPlusCallInfo *m_pComPlusCallInfo; // initialized in code:ComPlusCall.PopulateComPlusCallMethodDesc
};
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
// InstantiatedMethodDesc's are used for generics and
// come in four flavours, discriminated by the
// low order bits of the first field:
//
// 00 --> GenericMethodDefinition
// 01 --> UnsharedMethodInstantiation
// 10 --> SharedMethodInstantiation
// 11 --> WrapperStubWithInstantiations - and unboxing or instantiating stub
//
// ...
class InstantiatedMethodDesc : public MethodDesc
{
union {
RelativePointer<PTR_DictionaryLayout> m_pDictLayout; //SharedMethodInstantiation
RelativeFixupPointer<PTR_MethodDesc> m_pWrappedMethodDesc; // For WrapperStubWithInstantiations
};
public:
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
RelativePointer<PTR_Dictionary> m_pPerInstInfo; //SHARED
#else
PlainPointer<PTR_Dictionary> m_pPerInstInfo; //SHARED
#endif
private:
WORD m_wFlags2;
WORD m_wNumGenericArgs;
}
정리해 보면 대충 다음과 같은 관계로 해석됩니다.
IL = MethodDesc
(DynamicMethodDesc에 상속) == StoredSigMethodDesc
Instantiated = InstantiatedMethodDesc
FCall = FCallMethodDesc
NDirect = NDirectMethodDesc,
EEImpl = EEImplMethodDesc,
Array = ArrayMethodDesc
ComInterop = ComPlusCallMethodDesc,
Dynamic = DynamicMethodDesc
MethodDesc에는 IL 메서드인 경우 재미있는 필드가 하나 숨겨져 있는데, 이에 대해서는 다음의 글에서 제공하는 소스 코드에 나옵니다.
CLR Injection: Runtime Method Replacer
; https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/37549/CLR-Injection-Runtime-Method-Replacer
실행 시에 메서드 가로채기 - CLR Injection: Runtime Method Replacer 개선
; https://www.sysnet.pe.kr/2/0/942
private static IntPtr GetMethodAddress20SP2(MethodBase method)
{
unsafe
{
return new IntPtr(((int*)method.MethodHandle.Value.ToPointer() + 2));
}
}
이제 저 코드가 보이실 텐데요, MethodHandle의 값은 MethodDesc이므로 (int *)로 형변환해 +2를 더했으니 8바이트만큼 이동하게 됩니다. 즉, 기본적인 MethodDesc의 8바이트 이후에 나오는 포인터 값이 해당 메서드가 JIT된 기계어 코드의 주소인 것입니다. (여기서 유의할 점은, IL 코드 유형의 메서드에 한해 저 영역을 코드 주소로 활용할 수 있습니다.)
비록 MethodTable의 값을 Type.TypeHandle 속성을 통해 알 수 있지만, MethodDesc의 내부 필드 값을 이용해 접근하는 것도 가능합니다. 이에 관해서는 이전에
소개한 문서에서 다음의 그림으로 잘 설명하고 있는데,
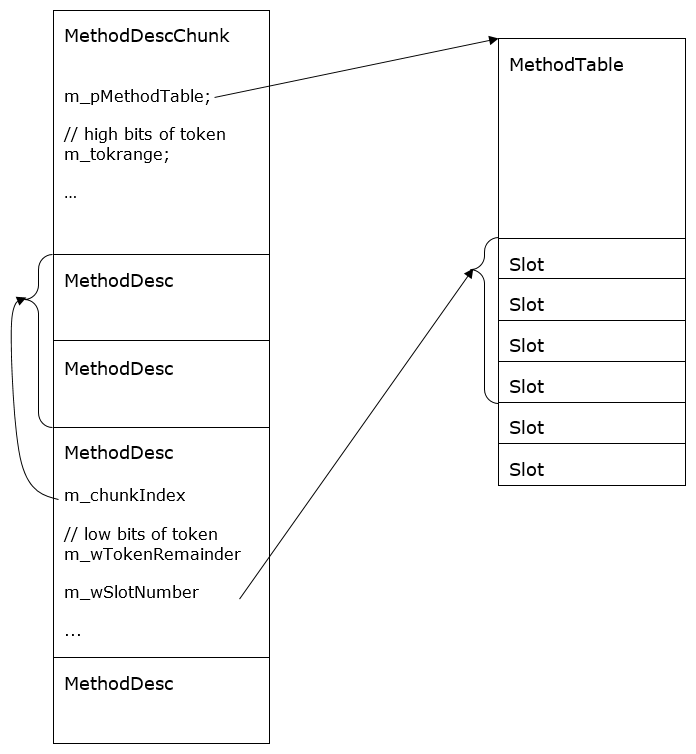
그러니까 MethodDesc은 "MethodDescChunk" 클래스의 정의에 따라,
class MethodDescChunk
{
RelativeFixupPointer<PTR_MethodTable> m_methodTable;
RelativePointer<PTR_MethodDescChunk> m_next;
BYTE m_size; // The size of this chunk minus 1 (in multiples of MethodDesc::ALIGNMENT)
BYTE m_count; // The number of MethodDescs in this chunk minus 1
UINT16 m_flagsAndTokenRange;
// Followed by array of method descs...
};
m_flagsAndTokenRange 필드 이후의 할당 영역에 테이블 형식으로 나열되어 있는 것입니다. 여기서 주의할 것은, MethodDesc은 각각의 메서드 유형에 따라 크기가 다르기 때문에 일괄적으로 고정 크기를 가진 인덱스로 접근할 수 없습니다. 대신 MethodDesc의 "chunkIndex"가 m_flagsAndTokenRange 필드 이후의 공간에 대해 8바이트 정렬을 기준으로 한 인덱스 값으로 표현된다는 점이 중요합니다.
의미인즉, 예를 들어 16 바이트 MethodDesc을 갖는 FCall 메서드 한 개와 8 바이트 MethodDesc을 갖는 IL 메서드 한 개가 연이어 있을 때 FCall 메서드의 MethodDesc에는 chunkIndex가 0인 반면, IL 메서드의 경우에는 (1이 아닌) 2가 되는 것입니다. 이런 규칙을 이용하면 해당 MethodDesc를 소유한 MethodDescChunk의 첫 번째 MethodDesc의 할당 위치를 계산할 수 있습니다. 어디... 한 번 계산해 볼까요? ^^
이를 위해 우선 모든 MethodDesc들이 공통적으로 갖는 MethodDescInternal 타입을 다음과 같이 정의하고,
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct MethodDescInternal
{
readonly ushort _wTokenRemainder;
public ushort TokenRemainder => _wTokenRemainder;
public uint Token
{
get { return ((uint)_wTokenRemainder & (uint)MethodDescFlags3.TokenRemainderMask) | (uint)CorTokenType.mdtMethodDef; }
}
readonly byte _chunkIndex;
public byte ChunkIndex => _chunkIndex;
readonly byte _bFlags2;
public MethodDescFlags2 Flags2
{
get
{
MethodDescFlags2 flag = (MethodDescFlags2)_bFlags2;
return flag;
}
}
readonly ushort _wSlotNumber;
public ushort SlotNumber => _wSlotNumber;
readonly ushort _wFlags;
public ushort Flags => _wFlags;
public MethodDescInternal(ushort tokenRemainder, byte chunkIndex, byte flags2, ushort slotNumber, ushort flags)
{
_wTokenRemainder = tokenRemainder;
_chunkIndex = chunkIndex;
_bFlags2 = flags2;
_wSlotNumber = slotNumber;
_wFlags = flags;
}
}
IntPtr로부터 이 값을 읽어들이는 코드를 만듭니다.
public class MethodDesc
{
// ...[생략]...
readonly MethodDescInternal _internal;
readonly IntPtr _address;
// ...[생략]...
protected MethodDesc(IntPtr address)
{
int offset = 0;
_internal = new MethodDescInternal
(
tokenRemainder: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
chunkIndex: address.ReadByte(ref offset),
flags2: address.ReadByte(ref offset),
slotNumber: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
flags: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset)
);
_address = address;
}
public static MethodDesc ReadFromAddress(IntPtr address)
{
return new MethodDesc(address);
}
}
그럼 MethodDescInternal로부터 ChunkIndex를 구할 수 있고,
int GetMethodDescIndex()
{
return _internal.ChunkIndex;
}
다음의 공식을 통해 MethodDescChunk의 시작 위치를 알 수 있습니다.
[methoddesc_address] - ( sizeof(MethodDescChunk) + chunkIndex * 8 )
위의 공식에서 아직 구하지 못한 MethodDescChunk의 크기는 다시 coreclr 소스 코드를 참조해 C# 코드로 포팅하고,
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct MethodDescChunkInternal
{
readonly IntPtr _methodTable;
public IntPtr MethodTable => _methodTable;
readonly IntPtr _next;
public IntPtr Next => _next;
readonly byte _size;
public int Size => _size;
readonly byte _count;
public int Count => _count;
readonly ushort _flagsAndTokenRange;
public ushort FlagsAndTokenRange => _flagsAndTokenRange;
public MethodDescChunkInternal(IntPtr methodTable, IntPtr next, byte size, byte count, ushort flagsAndTokenRange)
{
_methodTable = methodTable;
_next = next;
_size = size;
_count = count;
_flagsAndTokenRange = flagsAndTokenRange;
}
}
이에 대한 크기를 구하는 속성을 하나 추가해 주면,
public class MethodDescChunk
{
readonly MethodDescChunkInternal _internal;
readonly IntPtr _address;
public static uint SizeOf
{
get
{
return (uint)Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MethodDescChunkInternal));
}
}
// ...[생략]...
private MethodDescChunk(IntPtr address)
{
int offset = 0;
_internal = new MethodDescChunkInternal
(
methodTable: address.Add(address.ReadPtr(ref offset)),
next: address.ReadPtr(ref offset),
size: address.ReadByte(ref offset),
count: address.ReadByte(ref offset),
flagsAndTokenRange: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset)
);
_address = address;
}
public static MethodDescChunk ReadFromAddress(IntPtr ptr)
{
return new MethodDescChunk(ptr);
}
}
최종적으로 다음과 같이 MethodDescChunk를 반환하는 메서드를 MethodDesc 타입에 만들어 줄 수 있습니다.
public MethodDescChunk GetMethodDescChunk()
{
int offset = (int)MethodDescChunk.SizeOf + (GetMethodDescIndex() * 8);
IntPtr chunkPtr = _address - offset;
return MethodDescChunk.ReadFromAddress(chunkPtr);
}
MethodDescChunk를 구했다면, 그것의 첫 번째 필드가 저장하고 있는 MethodTable의 포인터로 Type.TypeHandle과 동일한 주솟값을 구할 수 있습니다.
public IntPtr GetMethodTablePtr()
{
return _internal.MethodTable;
}
참고로, MethodTable 역시 해당 주소로부터 coreclr의 C++ 소스 코드를 참고해 다음과 같이 대략적인 값을 구할 수 있습니다.
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct MethodTableInternal
{
readonly uint _dwFlags;
public uint Flags => _dwFlags;
// Base size of instance of this class when allocated on the heap
readonly uint _baseSize;
public uint BaseSize => _baseSize;
readonly ushort _wFlags2;
public ushort Flags2 => _wFlags2;
// Class token if it fits into 16-bits. If this is (WORD)-1, the class token is stored in the TokenOverflow optional member.
readonly ushort _wToken;
public ushort Token => _wToken;
// <NICE> In the normal cases we shouldn't need a full word for each of these </NICE>
readonly ushort _wNumVirtuals;
public ushort NumVirtuals => _wNumVirtuals;
readonly ushort _wNumInterfaces;
public ushort NumInterfaces => _wNumInterfaces;
/*
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
RelativePointer<PTR_MethodTableWriteableData> m_pWriteableData;
#else
PlainPointer<PTR_MethodTableWriteableData> m_pWriteableData;
#endif
*/
readonly IntPtr _pWriteableData;
/*
union {
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
RelativePointer<DPTR(EEClass)> m_pEEClass;
RelativePointer<TADDR> m_pCanonMT;
#else
PlainPointer<DPTR(EEClass)> m_pEEClass;
PlainPointer<TADDR> m_pCanonMT;
#endif
};
*/
readonly IntPtr _pEEClass_Or_pCanonMT;
/*
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
typedef RelativePointer<PTR_Dictionary> PerInstInfoElem_t;
typedef RelativePointer<DPTR(PerInstInfoElem_t)> PerInstInfo_t;
#else
typedef PlainPointer<PTR_Dictionary> PerInstInfoElem_t;
typedef PlainPointer<DPTR(PerInstInfoElem_t)> PerInstInfo_t;
#endif
union
{
PerInstInfo_t m_pPerInstInfo;
TADDR m_ElementTypeHnd;
TADDR m_pMultipurposeSlot1;
};
*/
readonly IntPtr _pPerInstInfo_Or_ElementTypeHnd_Or_pMultipurposeSlot1;
/*
union
{
#if defined(FEATURE_NGEN_RELOCS_OPTIMIZATIONS)
RelativePointer<PTR_InterfaceInfo> m_pInterfaceMap;
#else
PlainPointer<PTR_InterfaceInfo> m_pInterfaceMap;
#endif
TADDR m_pMultipurposeSlot2;
};
*/
readonly IntPtr _pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap;
// VTable and Non-Virtual slots go here
// Overflow multipurpose slots go here
// Optional Members go here
// See above for the list of optional members
// Generic dictionary pointers go here
// Interface map goes here
// Generic instantiation+dictionary goes here
public MethodTableInternal(uint dwFlags, uint baseSize, ushort wFlags2, ushort wToken, ushort wNumVirtuals,
ushort wNumInterfaces, IntPtr pWriteableData, IntPtr pEEClass_Or_pCanonMT,
IntPtr pPerInstInfo_Or_ElementTypeHnd_Or_pMultipurposeSlot1, IntPtr pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap)
{
_dwFlags = dwFlags;
_baseSize = baseSize;
_wFlags2 = wFlags2;
_wToken = wToken;
_wNumVirtuals = wNumVirtuals;
_wNumInterfaces = wNumInterfaces;
_pWriteableData = pWriteableData;
_pEEClass_Or_pCanonMT = pEEClass_Or_pCanonMT;
_pPerInstInfo_Or_ElementTypeHnd_Or_pMultipurposeSlot1 = pPerInstInfo_Or_ElementTypeHnd_Or_pMultipurposeSlot1;
_pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap = pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap;
}
}
public class MethodTable
{
readonly MethodTableInternal _internal;
readonly IntPtr _address;
public static uint SizeOf
{
get
{
return (uint)Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(MethodTableInternal));
}
}
public bool HasNonVirtualSlots()
{
return GetWEnumFlag(WFLAGS2_ENUM.enum_flag_HasNonVirtualSlots) != 0;
}
public uint GetHighEnumFlag(WFLAGS_HIGH_ENUM flag)
{
return _internal.Flags & (uint)flag;
}
public uint GetLowEnumFlag(WFLAGS_LOW_ENUM flag)
{
return (IsStringOrArray() ? ((uint)WFLAGS_LOW_ENUM.enum_flag_StringArrayValues & (uint)flag) : (_internal.Flags & (uint)flag));
}
public uint GetWEnumFlag(WFLAGS2_ENUM flag)
{
return _internal.Flags2 & (uint)flag;
}
public bool IsStringOrArray()
{
return HasComponentSize();
}
public bool HasComponentSize()
{
return GetHighEnumFlag(WFLAGS_HIGH_ENUM.enum_flag_HasComponentSize) != 0;
}
public bool HasSingleNonVirtualSlot()
{
return GetWEnumFlag(WFLAGS2_ENUM.enum_flag_HasSingleNonVirtualSlot) != 0;
}
public uint GetNumVirtuals()
{
return _internal.NumVirtuals;
}
private MethodTable(IntPtr address)
{
int offset = 0;
_internal = new MethodTableInternal(
dwFlags: address.ReadUInt32(ref offset),
baseSize: address.ReadUInt32(ref offset),
wFlags2: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
wToken: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
wNumVirtuals: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
wNumInterfaces: address.ReadUInt16(ref offset),
pWriteableData: address.ReadPtr(ref offset),
pEEClass_Or_pCanonMT: address.ReadPtr(ref offset),
pPerInstInfo_Or_ElementTypeHnd_Or_pMultipurposeSlot1: address.ReadPtr(ref offset),
pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap: address.ReadPtr(ref offset)
);
_address = address;
}
public static MethodTable ReadFromAddress(IntPtr ptr)
{
return new MethodTable(ptr);
}
}
이를 이용해 간단하게 평범한 인스턴스 메서드 하나에 대해 MethdDesc으로 다음과 같이 값을 덤프해 볼 수 있습니다.
private static unsafe void OutputMethodInfo(MethodInfo mi)
{
MethodDesc md = MethodDesc.ReadFromAddress(mi.MethodHandle.Value);
md.Dump(Console.Out);
}
/* 출력 결과
[MethodDesc 0x7ffe481f5cb8 - IL]
wTokenRemainder = c01b (Token = 600001b)
chunkIndex = e
bFlags2 = 00000021 (Flags2 == HasStableEntryPoint, IsEligibleForTieredCompilation)
wSlotNumber = d
wFlags = 0 (IsFullSlotNumber == False)
MethodTablePtr = 7ffe481f5cd0
*/
본문의 MethodDesc, MethodDescChunk, MethodTable 관련 타입들은 github의 프로젝트에 공개해 두었고,
DotNetSamples/WinConsole/PEFormat/DetourFunc/
; https://github.com/stjeong/DotNetSamples/tree/master/WinConsole/PEFormat/DetourFunc
이를 이용한 예제 코드는 이 글의 첨부 파일로 올렸습니다.
참고로, MethodTable은 heap에 할당된 객체를 통해서도 구할 수 있습니다.
C#에서 확인해 보는 관리 힙의 인스턴스 구조
; https://www.sysnet.pe.kr/2/0/1176
따라서, TypedReference를 이용해 GC Heap 상의 객체 주소를 얻어와 다음과 같이 조작하는 것으로 간단하게 MethodTable의 주소를 얻게 됩니다.
Program pg = new Program(); // Program 타입의 인스턴스 생성
TypedReference tr = __makeref(pg);
IntPtr objectPtr = **(IntPtr**)(&tr); // 인스턴스의 GC Heap 상에서의 주소 접근
Console.WriteLine($"Program object address in GC heap: {objectPtr.ToInt64():x}");
IntPtr methodTable = objectPtr.ReadPtr();
Console.WriteLine($"Method Table: {methodTable.ToInt64():x}"); // Program 타입의 MethodTable 테이블 주소
또한 MethodTable은 MethodDescChunk와 유사하게 가장 마지막 필드 이후의 공간에 주석에서 보는 바와 같이 다양한 값들을 보관하는 구조입니다.
// ...[생략]...
readonly IntPtr _pMultipurposeSlot2_Or_pInterfaceMap;
// VTable and Non-Virtual slots go here
// Overflow multipurpose slots go here
// Optional Members go here
// See above for the list of optional members
// Generic dictionary pointers go here
// Interface map goes here
// Generic instantiation+dictionary goes here
더 구해보고 싶지만, C++ 소스 코드가 점점 더 복잡해져서 오늘은 여기서 끝냅니다. (혹시 MethodTable의 나머지 공간을 분석하신 분들은 덧글 부탁드리겠습니다. ^^)
그 외에, 기타 웹상의 문서를 하나 보면,
.NET Internals and Code Injection
; https://ntcore.com/files/netint_injection.htm
coreclr의 CORINFO_CONTEXT_HANDLE 값이,
CHECK CheckContext(CORINFO_MODULE_HANDLE scopeHnd, CORINFO_CONTEXT_HANDLE context)
{
CHECK_MSG(scopeHnd != NULL, "Illegal null scope");
CHECK_MSG(((size_t) context & ~CORINFO_CONTEXTFLAGS_MASK) != NULL, "Illegal null context");
if (((size_t) context & CORINFO_CONTEXTFLAGS_MASK) == CORINFO_CONTEXTFLAGS_CLASS)
{
TypeHandle handle((CORINFO_CLASS_HANDLE) ((size_t) context & ~CORINFO_CONTEXTFLAGS_MASK));
CHECK_MSG(handle.GetModule() == GetModule(scopeHnd), "Inconsistent scope and context");
}
else
{
MethodDesc* handle = (MethodDesc*) ((size_t) context & ~CORINFO_CONTEXTFLAGS_MASK);
CHECK_MSG(handle->GetModule() == GetModule(scopeHnd), "Inconsistent scope and context");
}
CHECK_OK;
}
상황에 따라 MethodDesc*일 수도, 또는 TypeHandle - 아마도 MethodTable -의 값일 수도 있는 듯합니다. 또한, "What can be concluded is that CORINFO_METHOD_HANDLE only is a pointer to a MethodDesc class."라고 언급하는 것으로 CORINFO_METHOD_HANDLE == MethodDesc가 될 것입니다.
[이 글에 대해서 여러분들과 의견을 공유하고 싶습니다. 틀리거나 미흡한 부분 또는 의문 사항이 있으시면 언제든 댓글 남겨주십시오.]