C# - 인텔 CPU의 P-Core와 E-Core를 구분하는 방법
작년 말에 구매한 PC의 경우 엘더레이크 CPU를 장착하고 있는데요,
인텔 코어i9-12세대 12900K (엘더레이크) 정품
; http://prod.danawa.com/info/?pcode=15594887&cate=11341237
이 제품의 소개를 보면,
코어 수: 8+8 코어
스레드 수: 16+8 스레드
이런 식으로 표기가 되어 있습니다. 의미인즉, 8개의 P-Core와 8개의 E-Core로 나뉜다는 것인데, P-Core는 제 성능을 발휘할 수 있는 데다 Hyper-Threading도 지원을 하고 있어 8개의 P-Core가 16개의 스레드 수를 갖는 것이고, 반면 E-Core는 시스템의 작업 부하가 낮을 때 선택돼 저전력으로 동작하는 것으로 8개의 E-Core가 하이퍼스레딩 없이 각각 1개의 스레드를 담당할 수 있습니다.
이로 인해, 만약 개발자가 특정 스레드의 성능을 높이기 위해 Thread-affinity를 부여하고 싶다면 대상 코어가 P-Core인지, E-Core인지 확인해야 할 필요가 생긴 것입니다. 관련해서는 이미 인텔에서 자세한 자료를 배포하고 있는데요,
Game Dev Guide for Alder Lake Performance Hybrid Architecture
; https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/articles/guide/alder-lake-developer-guide.html
그래서 Win32 API에도 이를 위한 정보를 구하려면 GetSystemCpuSetInformation 함수를 이용하면 됩니다.
GetSystemCpuSetInformation function
; https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/getsystemcpusetinformation
SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION structure (winnt.h)
; https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winnt/ns-winnt-system_cpu_set_information
간단하게 C#으로 구현해 볼까요? ^^ 전체 소스 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace Console1
{
internal class NativeMethods
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
internal static extern uint GetCurrentThreadId();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true, EntryPoint = "GetSystemCpuSetInformation")]
static extern unsafe bool _GetSystemCpuSetInformation(byte* Information, uint BufferLength,
out uint ReturnedLength, IntPtr Process, uint Flags);
public static CpuInfo GetSystemCpuSetInformation()
{
IntPtr currentProcess = Process.GetCurrentProcess().Handle;
return GetSystemCpuSetInformation(currentProcess);
}
public static unsafe CpuInfo GetSystemCpuSetInformation(IntPtr processHandle)
{
List<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION> list = new List<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION>();
uint size;
do
{
bool result = NativeMethods.GetSystemCpuSetInformationRequiredSize(processHandle, out size);
if (result == false)
{
break;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[size];
fixed (byte* pBuffer = buffer)
{
result = _GetSystemCpuSetInformation(pBuffer, size, out _, processHandle, 0);
if (result == false)
{
break;
}
SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION* pItem = (SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION*)pBuffer;
int itemSize = sizeof(SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION);
if ((size % itemSize) != 0)
{
break;
}
uint loopCOunt = size / (uint)itemSize;
for (int i = 0; i < loopCOunt; i++)
{
list.Add(*pItem);
pItem++;
}
}
} while (false);
return new CpuInfo(list);
}
static unsafe bool GetSystemCpuSetInformationRequiredSize(IntPtr processHandle, out uint size)
{
NativeMethods._GetSystemCpuSetInformation(null, 0, out size, processHandle, 0);
uint lastError = NativeMethods.GetLastError();
if (lastError == (uint)Win32Error.ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern uint GetLastError();
}
public enum Win32Error
{
// MessageId: ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER
// MessageText:
// The data area passed to a system call is too small.
ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER = 122,
}
public enum CPU_SET_INFORMATION_TYPE
{
CpuSetInformation
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct CPU_INNER_STATUS
{
public byte Status;
public bool Parked
{
get { return (Status & (int)CpuStatusBit.Parked) == 1; }
}
public bool Allocated
{
get { return (Status & (int)CpuStatusBit.Allocated) == 1; }
}
public bool AllocatedToTargetProcess
{
get { return (Status & (int)CpuStatusBit.AllocatedToTargetProcess) == 1; }
}
public bool RealTime
{
get { return (Status & (int)CpuStatusBit.RealTime) == 1; }
}
[Flags]
enum CpuStatusBit
{
Parked = 0x01,
Allocated = 0x02,
AllocatedToTargetProcess = 0x04,
RealTime = 0x08,
}
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct CPU_STATUS
{
public byte AllFlags;
public CPU_INNER_STATUS CpuStatus;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct CPU_CLASS
{
public uint Reserved;
public byte SchedulingClass;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)]
public struct CPU_SET
{
[FieldOffset(0)]
public uint Id;
[FieldOffset(4)]
public short Group;
[FieldOffset(6)]
public byte LogicalProcessorIndex;
[FieldOffset(7)]
public byte CoreIndex;
[FieldOffset(8)]
public byte LastLevelCacheIndex;
[FieldOffset(9)]
public byte NumaNodeIndex;
[FieldOffset(10)]
public byte EfficiencyClass;
[FieldOffset(11)]
public CPU_STATUS FlagsAndStatus;
[FieldOffset(11)]
public CPU_CLASS Scheduling;
[FieldOffset(16)]
public ulong AllocationTag;
}
public class CpuInfo : IEnumerable<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION>
{
readonly List<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION> _list;
readonly bool _isHybrid;
readonly int _pcoreCount;
readonly int _ecoreCount;
internal CpuInfo(List<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION> list)
{
_list = list;
_pcoreCount = _list.Count((e) => e.IsPCore == true);
_ecoreCount = _list.Count((e) => e.IsECore == true);
_isHybrid = _pcoreCount > 0 && _ecoreCount > 0;
if (_isHybrid == false)
{
_pcoreCount = 0;
_ecoreCount = 0;
}
}
public int LogicalCoreCount => _list.Count;
public SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION this[int index] => _list[index];
public IEnumerator<SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION> GetEnumerator() => _list.GetEnumerator();
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() => _list.GetEnumerator();
public bool IsHybrid => _isHybrid;
public int PCoreCount => _pcoreCount;
public int ECoreCount => _ecoreCount;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION
{
public uint Size;
public CPU_SET_INFORMATION_TYPE Type;
public CPU_SET Set;
public override string ToString()
{
return $"{Set.LogicalProcessorIndex}: {Set.EfficiencyClass}";
}
public int Index
{
get { return Set.LogicalProcessorIndex; }
}
public bool IsPCore
{
get { return (int)Set.EfficiencyClass >= 1; }
}
public bool IsECore
{
get { return (int)Set.EfficiencyClass == 0; }
}
}
}
그래서 이를 이용해 다음과 같은 식으로 코딩할 수 있습니다.
using Console1;
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CpuInfo cpuInfo = NativeMethods.GetSystemCpuSetInformation();
if (cpuInfo.LogicalCoreCount == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("failed to call Win32 API GetSystemCpuSetInformation");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"IsHybridCPU: {cpuInfo.IsHybrid}");
if (cpuInfo.IsHybrid)
{
Console.WriteLine($"# of PCore: {cpuInfo.PCoreCount}");
Console.WriteLine($"# of ECore: {cpuInfo.ECoreCount}");
Console.WriteLine();
foreach (var item in cpuInfo)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[{item.Index}] IsPCore == {item.IsPCore}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"# of Cores: {cpuInfo.LogicalCoreCount}");
}
}
}
제 컴퓨터에서 위의 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같은 식으로 출력합니다.
IsHybridCPU: True
# of PCore: 16
# of ECore: 8
[0] IsPCore == True
[1] IsPCore == True
[2] IsPCore == True
[3] IsPCore == True
[4] IsPCore == True
[5] IsPCore == True
[6] IsPCore == True
[7] IsPCore == True
[8] IsPCore == True
[9] IsPCore == True
[10] IsPCore == True
[11] IsPCore == True
[12] IsPCore == True
[13] IsPCore == True
[14] IsPCore == True
[15] IsPCore == True
[16] IsPCore == False
[17] IsPCore == False
[18] IsPCore == False
[19] IsPCore == False
[20] IsPCore == False
[21] IsPCore == False
[22] IsPCore == False
[23] IsPCore == False
보는 바와 같이 P-core가 16개, E-core가 8개입니다. 이를 위한 구분은 SYSTEM_CPU_SET_INFORMATION 구조체에 있는 EfficiencyClass 필드의 값을 이용하면 되는데요, Intel 문서에 보면,
This value represents the power-to-performance ratio of a logical processor. Cores with a higher Efficiency Class value in the EfficiencyClass field have higher performance but lower power efficiency.
EfficiencyClass의 값이 높을수록 고성능이면서 전력 소비는 (성능을 높임에 따라) 비효율적이라고 합니다. 현재는 PCore인 경우 1, ECore인 경우 0이 나오는데요, 이 값의 타입이 byte인 것을 감안하면 또 다른 값이 향후 추가될 여지가 있습니다.
이를 이용해서 ECore를 바쁘게 만들어볼까요? ^^
ProcessThread.ProcessorAffinity 속성과 함께라면 다음과 같이 ECore 수만큼의 스레드를 생성하고 일정 시간 무한 루프를 돌아 부하를 줄 수 있습니다.
public class CpuInfo : IEnumerable
{
// ...[생략]...
public void LoadAllEcore_And_SeeTaskManagerCpuInfo_ForSeconds(int loadSeconds)
{
if (IsHybrid == false)
{
return;
}
List<Thread> threads = new List<Thread>();
EventWaitHandle startSignal = new EventWaitHandle(false, EventResetMode.ManualReset);
foreach (var item in _list)
{
if (item.IsPCore == true)
{
continue;
}
Thread t = new Thread((obj) =>
{
if (obj == null)
{
return;
}
int tid = (int)NativeMethods.GetCurrentThreadId();
SetThreadAffinity(tid, (int)obj);
startSignal.WaitOne();
long started = Environment.TickCount64;
while (true)
{
long diff = Environment.TickCount64 - started;
if (diff / 1000 > loadSeconds)
{
break;
}
}
});
threads.Add(t);
t.Start(item.Index);
}
startSignal.Set();
foreach (var item in threads)
{
item.Join();
}
}
static void SetThreadAffinity(int threadId, int coreIndex)
{
foreach (ProcessThread thread in Process.GetCurrentProcess().Threads)
{
if (threadId == thread.Id)
{
if (OperatingSystem.IsWindows())
{
thread.ProcessorAffinity = new IntPtr(1 << (coreIndex));
return;
}
}
}
}
}
위의 메서드를 호출하면 작업 관리자에서 다음과 같이 E-Core들의 사용량이 100%가 되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
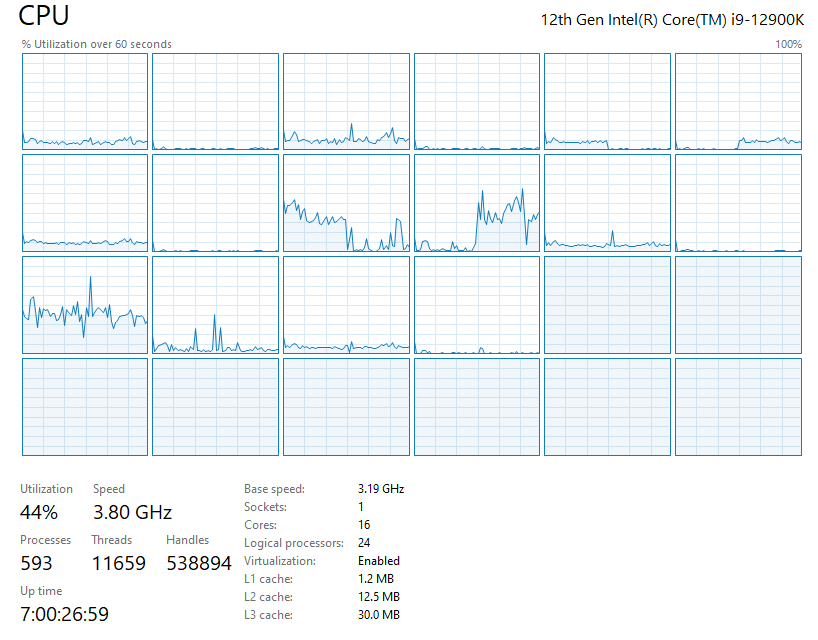
그런데, 다소 이상한 점이 있습니다. 저렇게 E-core를 모두 바쁘게 만들었더니 윈도우 운영체제의 UI 반응 속도가 전체적으로 느려졌습니다. 분명히, P-core들은 놀고 있음에도 컴퓨터 사용이 힘들 정도로 성능이 낮아지는데, 어쩌면 윈도우 11의 UI 관련 동작들을 기본적으로 E-core에서 스케줄링이 되도록 만든 것이 아닌가... 할 정도입니다.
(
첨부 파일은 이 글의 예제 코드를 포함합니다.)
[이 글에 대해서 여러분들과 의견을 공유하고 싶습니다. 틀리거나 미흡한 부분 또는 의문 사항이 있으시면 언제든 댓글 남겨주십시오.]