SQL Server TLS 통신을 위해 사용되는 키 길이 확인 방법
지난 글에서,
C# - Ubuntu + Microsoft.Data.SqlClient + SQL Server 2008 R2 연결 방법
; https://www.sysnet.pe.kr/2/0/13364
해당 현상은 (SQL Server 2012, 2014 버전은 테스트가 필요하지만, 적어도) SQL Server 2016 (버전 13.x)에서는 발생하지 않는다고 했습니다. 달리 말하면,
해당 버전부터는 2048비트 길이의 키를 가진 인증서가 생성돼 있다고 짐작할 수 있습니다.
정말 그런지 테스트해 봐야겠죠? ^^
마침 가지고 있던 테스트 PC 중에 SQL Server 2016 Express 버전이 설치된 것이 있길래
get_tds_cert.py를 실행했더니,
c:\temp> python get_tds_cert.py 192.168.100.50 1433
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "get_tds_cert.py", line 86, in <module>
s.connect(( hostname, port ))
socket.timeout: timed out
1433 포트로 연결이 안 됩니다. 실제로 SQL Server 2016 Express 측에는 1433 포트로 LISTENING하고 있는 소켓이 없습니다.
// SQL Server 2016 Experss 버전이 설치된 컴퓨터
C:\WINDOWS\system32> netstat -ano | findstr 1433
C:\WINDOWS\system32>
왜냐하면 Express 버전의 경우 동적 포트를 사용하게 되는데, 이 번호를 알려면 "
Sql Server Configuration Manager"를 실행해 다음과 같이 "SQL Server Network Configuration" 노드의 "Protocols for SQLEXPRESS" 속성 창을 통해 구해야 합니다.
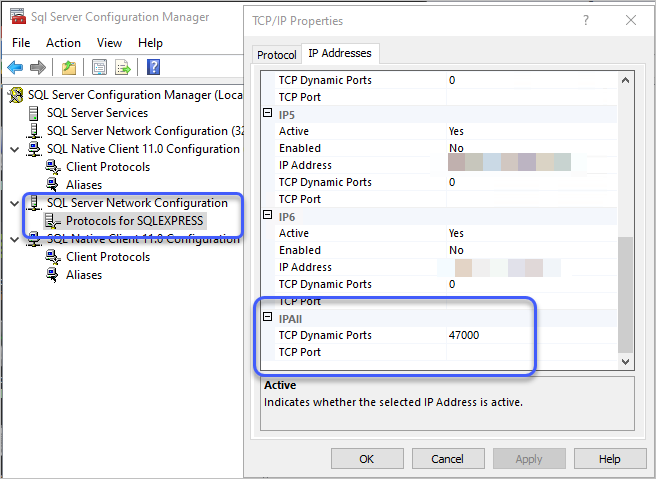
C:\WINDOWS\system32> netstat -ano | findstr 47000
TCP 0.0.0.0:47000 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 11588
TCP [::]:47000 [::]:0 LISTENING 11588
그럼, 이렇게 인증서를 조회할 수 있고,
c:\temp> python get_tds_cert.py 192.168.100.50 47000
# get_tdspacket: 0, tdspacket len: 43
# Header: {'type': 4, 'status': 1, 'length': 43, 'channel': 0, 'packet': 1, 'window': 0}
# Remaining tdspbuf length: 0
# Starting TLS handshake loop..
# Shaking (0/5)
# get_tdspacket: 0, tdspacket len: 1249
# Header: {'type': 18, 'status': 1, 'length': 1249, 'channel': 0, 'packet': 0, 'window': 0}
# Remaining tdspbuf length: 0
# Shaking (1/5)
# get_tdspacket: 0, tdspacket len: 59
# Header: {'type': 18, 'status': 1, 'length': 59, 'channel': 0, 'packet': 0, 'window': 0}
# Remaining tdspbuf length: 0
# Handshake completed, dumping certificates
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDADCCAeigAwIBAgIQH5dNyvwxI4ZI58THgmrvnjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADA7
MTkwNwYDVQQDHjAAUwBTAEwAXwBTAGUAbABmAF8AUwBpAGcAbgBlAGQAXwBGAGEA
...[생략]...
1ZLqpBiCaT6J9AG16QbYJMO0SMLTjHIuwgguSi+tUbydA734ugFtTJw0CHoR1K1x
2pqdlQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"BEGIN/END CERTIFICATE" 구간을 cer 파일로 저장해 윈도우 탐색기로 보면,
c:\temp> type 2016.cer
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDADCCAeigAwIBAgIQH5dNyvwxI4ZI58THgmrvnjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADA7
MTkwNwYDVQQDHjAAUwBTAEwAXwBTAGUAbABmAF8AUwBpAGcAbgBlAGQAXwBGAGEA
...[생략]...
1ZLqpBiCaT6J9AG16QbYJMO0SMLTjHIuwgguSi+tUbydA734ugFtTJw0CHoR1K1x
2pqdlQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
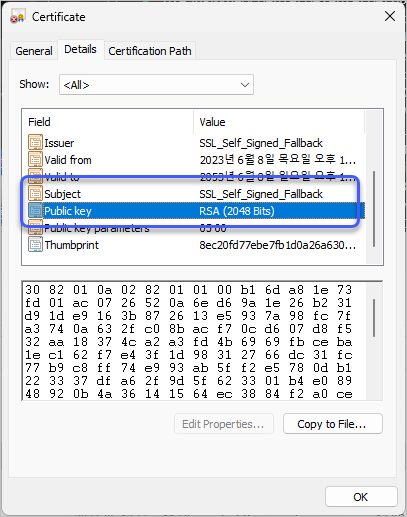
2048비트 길이의 키가 사용된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
참고로,
get_tds_cert.py의 소스코드는 TDS(Tabular data stream) Protocol 중 인증서를 가져오는 부분까지만 구현하고 있기 때문에 원한다면 C# 소스코드로 쉽게(?) 포팅할 수 있을 것입니다. ^^
import sys
import pprint
import struct
import socket
import ssl
from time import sleep
# Standard "HELLO" message for TDS
prelogin_msg = bytearray([ 0x12, 0x01, 0x00, 0x2f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x1a, 0x00, 0x06, 0x01, 0x00, 0x20,
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x00, 0x21, 0x00, 0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x22, 0x00, 0x04, 0x04, 0x00, 0x26, 0x00,
0x01, 0xff, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 ])
# Prep Header function
def prep_header(data):
data_len = len(data)
prelogin_head = bytearray([ 0x12, 0x01 ])
header_len = 8
total_len = header_len + data_len
data_head = prelogin_head + total_len.to_bytes(2, 'big')
data_head += bytearray([ 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00])
return data_head + data
def read_header(data):
if len(data) != 8:
raise ValueError("prelogin header is > 8-bytes", data)
format = ">bbhhbb"
sct = struct.Struct(format)
unpacked = sct.unpack(data)
return { "type": unpacked[0],
"status": unpacked[1],
"length": unpacked[2],
"channel": unpacked[3],
"packet": unpacked[4],
"window": unpacked[5]
}
tdspbuf = bytearray()
def recv_tdspacket(sock):
global tdspbuf
tdspacket = tdspbuf
header = {}
for i in range(0,5):
tdspacket += sock.recv(4096)
print("\n# get_tdspacket: {}, tdspacket len: {} ".format(i, len(tdspacket)))
if len(tdspacket) >= 8:
header = read_header(tdspacket[:8])
print("# Header: ", header)
if len(tdspacket) >= header['length']:
tdspbuf = tdspacket[header['length']:]
print("# Remaining tdspbuf length: {}\n".format(len(tdspbuf)))
return header, tdspacket[8:header['length']]
sleep(0.05)
# Ensure we have a commandline
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage: {} <hostname> <port>".format(sys.argv[0]))
sys.exit(1)
hostname = sys.argv[1]
port = int(sys.argv[2])
# Setup SSL
if hasattr(ssl, 'PROTOCOL_TLS'):
sslProto = ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS
else:
sslProto = ssl.PROTOCOL_SSLv23
sslctx = ssl.SSLContext(sslProto)
sslctx.check_hostname = False
tls_in_buf = ssl.MemoryBIO()
tls_out_buf = ssl.MemoryBIO()
# Create the SSLObj connected to the tls_in_buf and tls_out_buf
tlssock = sslctx.wrap_bio(tls_in_buf, tls_out_buf)
# create an INET, STREAMing socket
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.setblocking(0)
s.settimeout(1)
# Connect to the SQL Server
s.connect(( hostname, port ))
# Send the first TDS PRELOGIN message
s.send(prelogin_msg)
# Get the response and ignore. We will try to negotiate encryption anyway.
header, data = recv_tdspacket(s)
while header['status']==0:
header, ext_data = recv_tdspacket(s)
data += ext_data
print("# Starting TLS handshake loop..")
# Craft the packet
for i in range(0,5):
try:
tlssock.do_handshake()
print("# Handshake completed, dumping certificates")
peercert = ssl.DER_cert_to_PEM_cert(tlssock.getpeercert(True))
print(peercert)
sys.exit(0)
except ssl.SSLWantReadError as err:
# TLS wants to keep shaking hands, but because we're controlling the R/W buffers it throws an exception
print("# Shaking ({}/5)".format(i))
tls_data = tls_out_buf.read()
s.sendall(prep_header(tls_data))
# TDS Packets can be split over two frames, each with their own headers.
# We have to concat these for TLS to handle nego properly
header, data = recv_tdspacket(s)
while header['status']==0:
header, ext_data = recv_tdspacket(s)
data += ext_data
tls_in_buf.write(data)
print("# Handshake did not complete / exiting")
[이 글에 대해서 여러분들과 의견을 공유하고 싶습니다. 틀리거나 미흡한 부분 또는 의문 사항이 있으시면 언제든 댓글 남겨주십시오.]