눈으로 확인하는 LayoutKind 옵션 효과
와~~~ ^^ 재미있는 거 하나 또 배웠습니다. ^^
[제목] 객체의 메모리 레이아웃에 대하여
; http://www.csharpstudy.com/network/DevNote/Article/1009
이에 대해 제가 미진하게 테스트해서 올린 글이 있었는데요.
LayoutKind 옵션에 대해
; https://www.sysnet.pe.kr/2/0/1557
이 글에 대해 원글 저자이신 Alex님이 덧글을 달아주셨고 그래서 다시 정리해서 이렇게 글을 남깁니다. ^^
"
[제목] 객체의 메모리 레이아웃에 대하여" 글에서 소개한 다음의 내용을 직접 확인하는 방법을 알아보겠습니다.
Sequential Layout은 Managed Memory에서 마샬링을 사용해 Unmanaged Memory로 옮길 때 각 필드의 순서가 Unmanaged Memory에서 유지되는 레이아웃이다. 위의 예제에서 MyStruct 구조체는 [StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]을 사용하고 있는데, 이는 Managed 메모리 영역에서는 순서가 어떨지 모르지만, Unmanaged Memory로 옮겨질 때는 반드시 필드 순서대로 데이타가 옮겨진다는 것을 의미한다.
즉, 위의 글에 따라 LayoutKind 옵션을 정리하면 다음과 같은 식입니다.
그럼 이 옵션들이 실제로 그렇게 동작하는지 이제 확인해 보겠습니다. ^^
테스트 예제는 다음과 같이 구성해 보았습니다.
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Auto)]
class MyClassA
{
public int i = 1;
public string s = "2";
public double d = 2;
public byte b = 3;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1)]
class MyClassB
{
public int i = 1;
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 16)]
public string s = "2";
public double d = 3;
public byte b = 4;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit, Pack = 1)]
class MyClassC
{
[FieldOffset(0)]
public int i = 1;
[FieldOffset(4)]
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 16)]
public string s = "2";
[FieldOffset(4 + 16)]
public double d = 3;
[FieldOffset(4 + 16 + 8)]
public byte b = 4;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClassA var1 = new MyClassA();
MyClassB var2 = new MyClassB();
MyClassC var3 = new MyClassC();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
windbg를 이용해 3개의 객체가 어떤 레이아웃으로 관리 힙에 할당되어 있는지 보려면 다음과 같은 명령어 과정을 거치면 됩니다.
0:006> .loadby sos clr
0:000> !name2ee *!ConsoleApplication1.MyClassA
Module: 720c1000
Assembly: mscorlib.dll
--------------------------------------
Module: 007f2ed4
Assembly: ConsoleApplication1.exe
Token: 02000002
MethodTable: 007f38b4
EEClass: 007f13ac
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassA
0:004> !dumpheap -mt 007f38b4
Address MT Size
02492508 007f38b4 28
Statistics:
MT Count TotalSize Class Name
007f38b4 1 28 ConsoleApplication1.MyClassA
Total 1 objects
0:004> !dumpobj 02492508
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassA
MethodTable: 007f38b4
EEClass: 007f13ac
Size: 28(0x1c) bytes
File: d:\...\bin\Debug\ConsoleApplication1.exe
Fields:
MT Field Offset Type VT Attr Value Name
724d3c50 4000001 10 System.Int32 1 instance 1 i
724d2300 4000002 c System.String 0 instance 02492524 s
724cb5a0 4000003 4 System.Double 1 instance 2.000000 d
724d36b4 4000004 14 System.Byte 1 instance 3 b
보시는 바와 같이 Auto 레이아웃의 MyClassA는 관리 힙에 할당된 필드의 메모리 순서가 제멋대로입니다. 이런 식으로 MyClassB, MyClassC를 확인하면 다음과 같습니다.
0:004> !dumpobj 02492534
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassB
MethodTable: 007f394c
EEClass: 007f1400
Size: 28(0x1c) bytes
File: d:\...\bin\Debug\ConsoleApplication1.exe
Fields:
MT Field Offset Type VT Attr Value Name
724d3c50 4000005 10 System.Int32 1 instance 1 i
724d2300 4000006 c System.String 0 instance 02492524 s
724cb5a0 4000007 4 System.Double 1 instance 3.000000 d
724d36b4 4000008 14 System.Byte 1 instance 4 b
0:004> !dumpobj 02492550
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassC
MethodTable: 007f39e4
EEClass: 007f14c8
Size: 40(0x28) bytes
File: d:\...\bin\Debug\ConsoleApplication1.exe
Fields:
MT Field Offset Type VT Attr Value Name
724d3c50 4000009 4 System.Int32 1 instance 1 i
724d2300 400000a 8 System.String 0 instance 02492524 s
724cb5a0 400000b 18 System.Double 1 instance 3.000000 d
724d36b4 400000c 20 System.Byte 1 instance 4 b
이 정도면 관리 메모리에서의 필드 배치 검증은 되었겠죠! ^^
그럼, 비관리 메모리로 마샬링되었을 때의 필드 배치는 어떤 방법을 통해서 알 수 있을까요?
간단하게 Marshal.StructureToPtr 메서드를 이용하면 가능합니다. 따라서 이전 예제에서 다음과 같은 코드를 추가해 주면 됩니다.
int sizeofA = Marshal.SizeOf(var1);
int sizeofB = Marshal.SizeOf(var2);
int sizeofC = Marshal.SizeOf(var3);
IntPtr ptrA = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(sizeofA);
Marshal.StructureToPtr(var1, ptrA, false);
IntPtr ptrB = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(sizeofB);
Marshal.StructureToPtr(var2, ptrB, false);
IntPtr ptrC = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(sizeofC);
Marshal.StructureToPtr(var3, ptrC, false);
그런데, 이 예제를 실행시키면 2군데에서 런타임 오류가 발생합니다. MyClassA 타입의 경우 Auto Layout이 사용되었기 때문에 unmanaged 메모리로의 변환은 물론 크기까지도 가늠할 수 없기 때문에 Marshal.SizeOf 및 StructureToPtr 메서드에서 각각 다음과 같은 오류가 발생합니다.
Unhandled Exception: System.ArgumentException: Type 'ConsoleApplication1.MyClassA' cannot be marshaled as an unmanaged structure; no meaningful size or offset can be computed.
at System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.SizeOfHelper(Type t, Boolean throwIfNotMarshalable)
at System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.SizeOf(Object structure)
at ConsoleApplication1.Program.Main(String[] args) in d:\...\ConsoleApplication1\Program.cs:line 52
Unhandled Exception: System.ArgumentException: The specified structure must be blittable or have layout information.
Parameter name: structure
at System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.InternalStructureToPtr(Object structure, IntPtr ptr, Boolean fDeleteOld)
at System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.StructureToPtr(Object structure, IntPtr ptr, Boolean fDeleteOld)
at ConsoleApplication1.Program.Main(String[] args) in d:\...\ConsoleApplication1\ConsoleApplication1\Program.cs:line 57
따라서 그 부분은 주석 처리를 하고 진행합니다. ^^ (말인즉, MyClassA는 비관리 메모리의 필드 배치를 확인할 수 없습니다.)
int sizeofA = 100; //Marshal.SizeOf(var1);
int sizeofB = Marshal.SizeOf(var2);
int sizeofC = Marshal.SizeOf(var3);
IntPtr ptrA = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(sizeofA);
// Marshal.StructureToPtr(var1, ptrA, false);
이제 Console.ReadLine 부근에 BP(BreakPoint)를 잡은 후 예제를 Visual Studio에서 실행하면 ptrB, ptrC의 주소에 직렬화된 객체의 필드 값들을 확인할 수 있습니다.
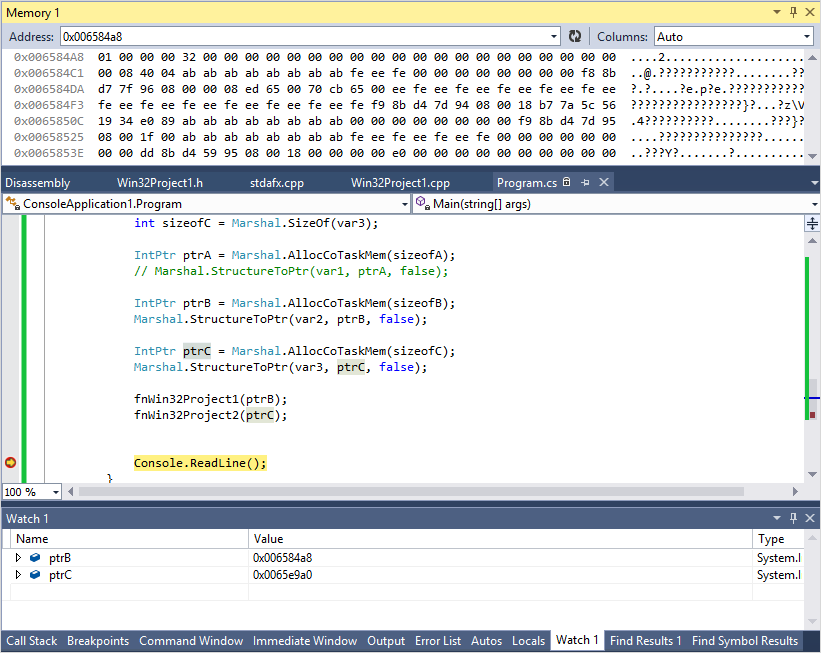
이를 통해 ptrB, ptrC의 값들을 하나씩 분석해 보면 다음과 같은 결과가 나옵니다.
== ptrB ==
0x006584A8 01 00 00 00 32 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ....2....................
0x006584C1 00 08 40 04 ab ab ab ab ab ab ab ab fe ee fe 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 f8 8b ..@.???????????........??
01 00 00 00 : int 4bytes == 0x00000001
32 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 : TStr 16bytes == "2"
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 08 40 : double 8bytes == 3 (부동 소수점 표현)
04 : byte 1byte == 4
== ptrC ==
0x00DAE988 01 00 00 00 32 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ....2....................
0x00DAE9A1 00 08 40 04 ab ab ab ab ab ab ab ab fe ee fe 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 9e 7e ..@.???????????........?~
01 00 00 00 : int 4bytes == 0x00000001
32 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 : TStr 16bytes == "2"
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 08 40 : double 8bytes == 3 (부동 소수점 표현)
04 : byte 1byte == 4
보시는 것처럼 MyClassB, MyClassC의 필드 배치가 정확하게 일치합니다. 따라서 Sequential, Explicit 유형의 클래스는 비관리 메모리에서 필드의 정의에 따른 위치가 그대로 보존됨을 알 수 있습니다.
이 때문에 일단 이런 식으로 직렬화된 클래스는 다음과 같이 C/C++에 전달하는 것도 가능합니다.
// ==== C++ Win32 DLL
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct tagMyClassB
{
int i;
char s[16];
double d;
BYTE b;
} MyClassB;
typedef struct tagMyClassC
{
int i;
char s[16];
double d;
byte b;
} MyClassC;
WIN32PROJECT1_API void fnWin32Project1(MyClassB *ptr)
{
printf("i: %d\n", ptr->i);
printf("s: %S\n", ptr->s);
printf("d: %lf\n", ptr->d);
printf("b: %d\n\n", ptr->b);
}
WIN32PROJECT1_API void fnWin32Project2(MyClassC *ptr)
{
printf("i: %d\n", ptr->i);
printf("s: %S\n", ptr->s);
printf("d: %lf\n", ptr->d);
printf("b: %d\n\n", ptr->b);
}
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
// ...[생략]...
class Program
{
[DllImport("Win32Project1.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
static extern void fnWin32Project1(IntPtr cl);
[DllImport("Win32Project1.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
static extern void fnWin32Project2(IntPtr cl);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClassA var1 = new MyClassA();
MyClassB var2 = new MyClassB();
MyClassC var3 = new MyClassC();
// ...[생략]...
fnWin32Project1(ptrB);
fnWin32Project2(ptrC);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
(취소시킨) 아래의 글을 쓰면서 제가 가장 궁금했던 것은,
LayoutKind 옵션에 대해
; https://www.sysnet.pe.kr/2/0/1557
굳이 Sequential에서 관리/비관리 메모리의 구조가 다를 이유가 있었을까 하는 점입니다. 제가 생각하기에는 그것이 매우 비효율적인 작업이라고 여겼기 때문인데요. 이번 테스트를 통해서 오히려 그것이 효율적인 메모리 관리임을 알게 되었습니다.
MyClassB, MyClassC의 windbg 결과를 좀 더 살펴보면 왜 그것이 효율적인지에 대한 답이 나옵니다.
0:004> !name2ee *!ConsoleApplication1.MyClassB
Module: 720c1000
Assembly: mscorlib.dll
--------------------------------------
Module: 00922ed4
Assembly: ConsoleApplication1.exe
Token: 02000003
MethodTable: 0092394c
EEClass: 00921418
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassB
0:004> !dumpheap -mt 0092394c
Address MT Size
025c25bc 0092394c 28
Statistics:
MT Count TotalSize Class Name
0092394c 1 28 ConsoleApplication1.MyClassB
Total 1 objects
위의 결과를 보면 Sequential로 지정된 MyClassB에 할당된 객체의 크기는 총 28바이트입니다. 반면 Explicit로 지정된 MyClassC에 할당된 객체의 크기는 40바이트로 나옵니다.
0:004> !name2ee *!ConsoleApplication1.MyClassC
Module: 720c1000
Assembly: mscorlib.dll
--------------------------------------
Module: 00922ed4
Assembly: ConsoleApplication1.exe
Token: 02000004
MethodTable: 009239e4
EEClass: 009214e0
Name: ConsoleApplication1.MyClassC
0:004> !dumpheap -mt 009239e4
Address MT Size
025c25d8 009239e4 40
Statistics:
MT Count TotalSize Class Name
009239e4 1 40 ConsoleApplication1.MyClassC
Total 1 objects
왜 이렇게 메모리 크기의 차이가 심하게 발생하는지 각각에 할당된 힙 메모리 사용을 한번 살펴볼까요? ^^
0:004> db 025c25bc
025c25bc 4c 39 92 00 00 00 00 00-00 00 08 40 ac 25 5c 02 L9.........@.%\.
025c25cc 01 00 00 00 04 00 00 00-00 00 00 00 e4 39 92 00 .............9..
025c25dc 01 00 00 00 ac 25 5c 02-00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 .....%\.........
4c 39 92 00 : 0x0092394c == MethodTable
00 00 00 00-00 00 08 40 : Offset 위치 0x04 - System.Double 값
ac 25 5c 02 : Offset 위치 0x0c - System.String의 힙 주소 == 0x025c25ac
01 00 00 00 : Offset 위치 0x10 - System.Int32 값
04 00 00 00 : Offset 위치 0x14 - System.Byte 값 (마지막 4바이트 정렬)
Sequential 형식의 MyClassB는 24바이트에 syncblock 4바이트까지 더해져 총 28바이트가 소비됩니다.
반면 Explicit 형식의 MyClassC는 중간에 쓸데없이 12바이트 영역의 메모리가 차지하게 됩니다.
0:004> db 025c25d8
025c25d8 e4 39 92 00 01 00 00 00-ac 25 5c 02 00 00 00 00 .9.......%\.....
025c25e8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00-00 00 00 00 00 00 08 40 ...............@
025c25f8 04 00 00 00 00 00 01 00-18 7d 4d 72 00 00 00 00 .........}Mr....
e4 39 92 00 : 0x009239e4 == MethodTable
01 00 00 00 : Offset 위치 0x04 - System.Int32 값
ac 25 5c 02 : Offset 위치 0x08 - System.String의 힙 주소 == 0x025c25ac
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 : Explicit로 인해 필요 없이 소비된 12바이트
00 00 00 00 00 00 08 40 : Offset 위치 0x18 - System.Double 값
04 00 00 00 : Offset 위치 0x20 - System.Byte 값 (마지막 4바이트 정렬)
즉, 관리 메모리와 비관리 메모리의 레이아웃을 맞추기 위해 Explicit는 오히려 관리 메모리의 저장 효율을 떨어뜨리고 있는 것입니다. 물론, 1:1로 매핑되기 때문에 비관리 메모리로의 복사는 빠를 것입니다.
이로 인해 결론이 정리되는군요. ^^
(
첨부 파일은 위의 코드에 사용된 예제를 담고 있습니다.)
[이 글에 대해서 여러분들과 의견을 공유하고 싶습니다. 틀리거나 미흡한 부분 또는 의문 사항이 있으시면 언제든 댓글 남겨주십시오.]